-
December 19, 2025

A few years in QA, and you’ll inherit test suites that feel more like an archaeological dig site: old ideas, ancient workflows, and test cases nobody can understand or delete. With every sprint, there are more tests. With every bug, there is another regression case.
Test case prioritization provides a path out of the spiral. It determines which tests should run first, most often, and fastest, based on factors like business value, user behavior, past failures, and risk.
With AI entering the picture, tools can also accelerate prioritization and modernization if used accurately.
What is Test Case Prioritization?
Test case prioritization is the process of scheduling tests in sequence so that the important ones execute first. In the real world, prioritization serves both a technical and financial end.
The cost to fix a bug found during implementation is about six times higher than one identified during design. In the early stages, code is limited, and bugs are easy to find. As the software and its codebase grow, anomalies have more surface area to hide, and are more likely to slip through quality gates.
This is concerning because a survey found that two-thirds of respondents acknowledged their organization regularly deploys untested code, either accidentally or to meet expedited release schedules.
Test prioritization is a safety net against this scenario.
How Test Prioritization Helps Maintain Software Quality
Not all tests are equal.
Some validate critical flows: payments, authentication, account recovery, order processing, and data integrity.
Others check cosmetic UI behavior or low-traffic user flows.
When time is limited, prioritization pushes critical tests to the forefront. That means bugs with real financial and reputational impact are always caught, as those tests are executed first.
Instead of falling back on random “smoke checks” and intuition, teams can utilize test prioritization to focus their limited time and effort on high-risk, high-value software areas. Tools like TestWheel facilitate this protocol by leveraging analytics, historical defect patterns, change impact analysis, and business priorities.
Prioritization also helps prevent instability in app features known to be fragile or those that change frequently, carry complex dependencies, or have a history of breaking. These features are tested on priority, meaning that a shorter test cycle can still cover liability areas.
Direct Benefits of Test Prioritization
Test prioritization offers measurable benefits for engineering teams and the business as a whole. It helps build high-impact, intelligence-driven pipelines that catch the important bugs early and allocate QA effort when it drops the best ROI.
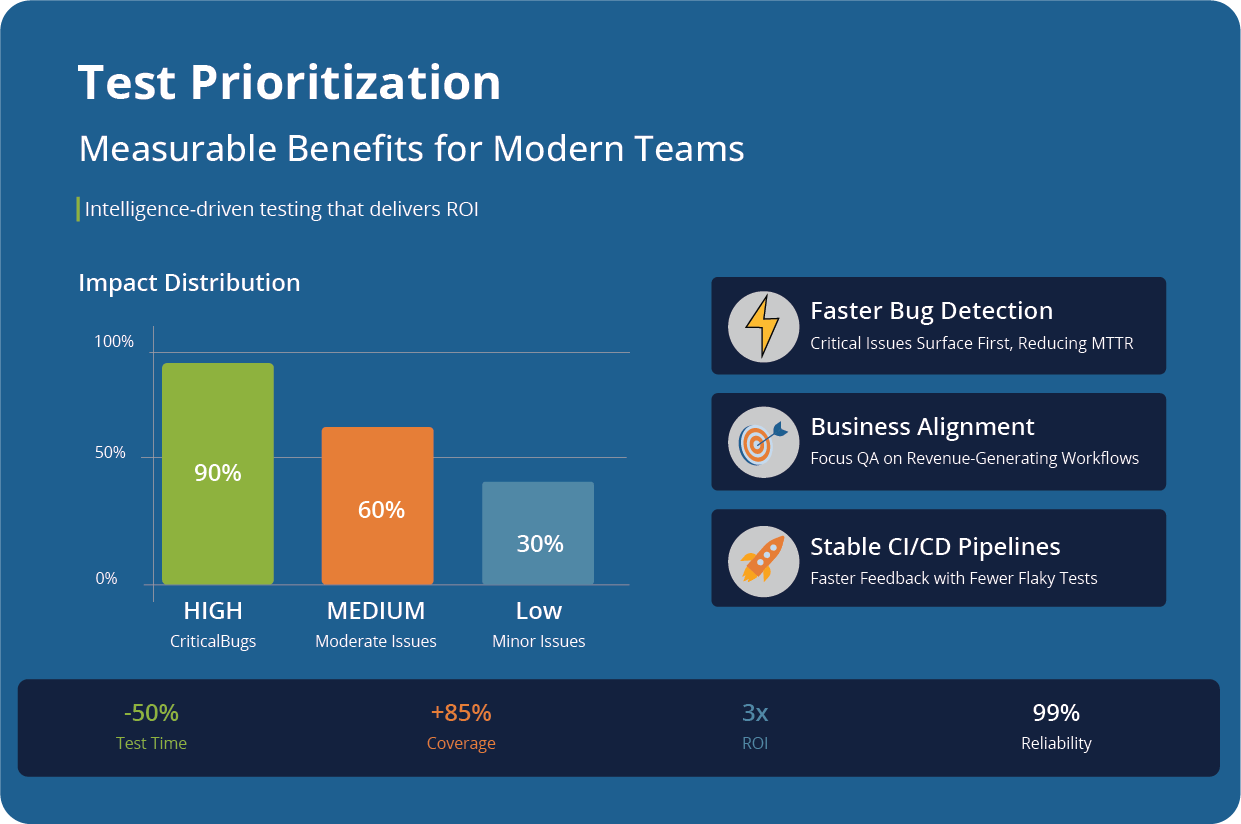
Faster Detection of High-Impact Defects
Prioritization top-ranks tests most likely to reveal severe, revenue-affecting bugs. Critical bugs show up first, so devs can fix them faster.
Teams prevent expensive production incidents, and decrease the workload for themselves by finding bugs when they are cheapest to fix.
Shorter Test Cycles Without Safety Gaps
Most teams can’t run entire test suites with every commit. Prioritization lets QA cover its bases even when running on short cycle times. High-priority tests and test cases go first, while lower-value tests run nightly or in regression.
Aligns Test Effort with Business Value
Test suites tend to drift over time. Prioritization keeps the two in line so QA focuses on what helps users and revenue.
P0 tests monitor core, money-making workflows (checkout, login, billing). Engineering effort goes from “testing as much as you can” to “testing what matters”.
Stable CI/CD Pipelines
Unprioritized test suites slow down pipelines by trying to cover too much. The result is inconsistent feedback. Fewer redundant tests help pipelines run faster.
Flaky, low-value tests can be quarantined or deprioritized without blocking releases. At the same time, devs get clearer, more actionable feedback.
Better Risk Management
Prioritization puts true risk into context and provides a path of action. High-risk modules undergo more scrutiny and get tested earlier. Stakeholders also get clarity on what is tested, what isn’t, and why.
Test Prioritization Techniques
This isn’t an exhaustive list, but these are the techniques used most commonly to prioritize software tests.
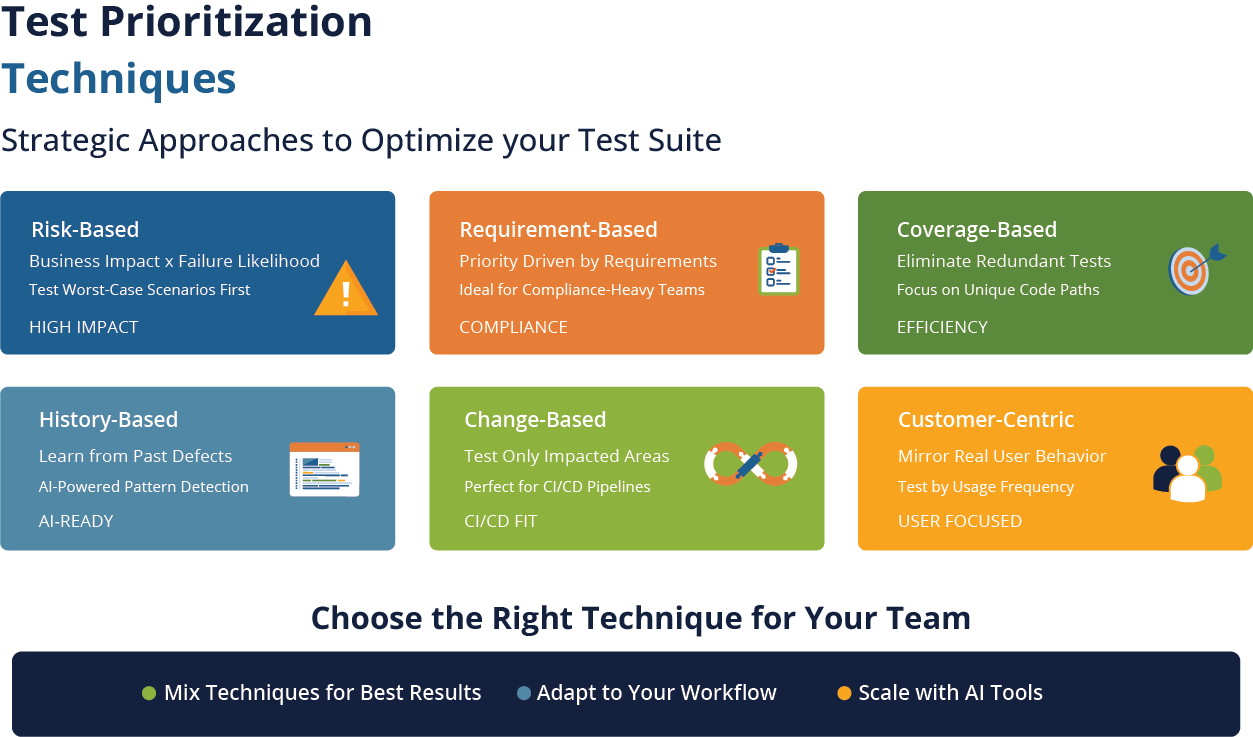
Risk-Based Prioritization
The question this asks is: What is the worst thing that can break, and how likely is it?
Testers evaluate test cases based on business impact, likelihood of failure, and frequency of code changes. Often, teams will find that too many test cases validate features used by only a few customers while a couple of brittle UI tests cover high-traffic workflows.
Requirement-Based Prioritization
Here, requirements determine test priority. You first test the features driven by the more important requirements. Compliance-heavy organizations especially use this technique, as it lays out tests clearly on the spectrum between “this requirement keeps us out of jail” and “these test cases are P0.”
The technique also helps stabilize test situations in which the product has dozens of stakeholders with different, sometimes opposing opinions. Requirements become the center of gravity and keep everyone on the same page.
Coverage-Based Prioritization
Coverage-based prioritization checks if multiple test cases cover the same workflow and gets rid of the redundant ones. This sequence pushes edge cases or integration-heavy scenarios to the front of the line.
History-Based Prioritization
Bugs tend to cluster. Teams can analyze defect history to create an accurate risk profile, based on real-world occurrences rather than assumptions (even educated ones).
Let’s say one module has seen production issues for the last 3 releases. Tests covering this module run first.
AI-enabled testing tools like TestWheel are especially effective in this space. The AI engine can flag patterns in historical test and production data to narrow down targeting for extensive testing.
Change-Based Prioritization
This technique aligns more closely with CI/CD realities. Each code change is studied with coverage maps, dependency graphs, or AI. Only tests related to impacted areas are executed.
High-performing DevOps teams frequently use this technique to run faster, more reliable releases.
Customer-Centric Prioritization
Simply put, your test suite should reflect how your customers use your product. For instance, if 60% of your users interact with checkout, 50% with search, and 12% with advanced filters, test those features in that order of importance.
Modernizing Legacy Test Cases for Prioritization
You cannot prioritize test suites that are not readable, maintainable, and duplicative. Most legacy test suites, unfortunately, carry artifacts and data somewhere lying between code patches and Tolstoy chapters.
So, consider this approach to take the first step.
Start with an Audit
Look at each test and ask:
- Is this test case still relevant?
- Does the feature covered by this test case still exist?
- Has this test actually caught a bug in the past 6 months?
- Is this test unique, or do we have multiple variations of it?
Take an honest look to see if your test suite is outdated, duplicated, or no longer tied to any active function.
Refactor into Modern Structures
Rework legacy tests to contain:
- Clear title
- Preconditions
- Focused steps
- Explicit expected results
Convert legacy manual test cases to concise, unambiguous, and automation-ready formats.
Merge and Parameterize
Take those 15 test cases that are only different by username, merge them, and create one parameterized test that covers the lot.
Assign Priorities
Once your tests are modernized, score them on three categories:
- P0: Business-critical. Run on every build or commit.
- P1: Important but not critical. Run nightly or before release.
- P2: Nice-to-have. Run in full regression or as often as needed.
How AI Can Help Establish Test Prioritization
In its ideal form, AI engines can basically act as junior testers who get things done faster than their human version. TestWheel, for instance, uses AI as a multiplier for good human judgment, rather than a replacement.
TestWheel uses AI to read, refactor, classify, and generate test cases at a speed that would take humans days or weeks, while keeping the human tester always in control.
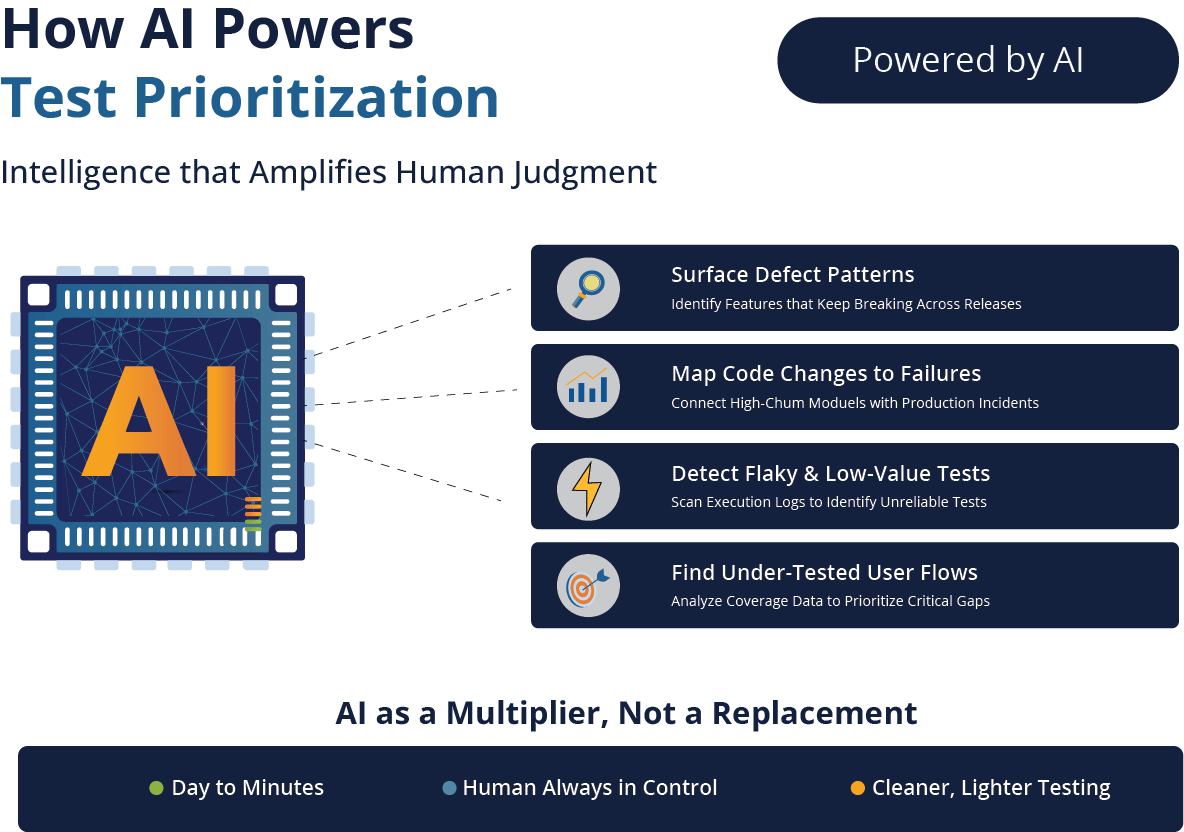
AI for Test Prioritization
Most QA teams are dealing with enormous datasets on defect history, code churn, execution logs, dashboards, coverage reports, and usage analytics.
Most of this doesn’t get used for day-to-day operations, especially when deciding the test sequence for execution.
TestWheel’s AI can:
- Surface patterns in defect history, especially for features that keep breaking.
- Map code change frequency to failures.
- Scan test execution logs to find flaky or low-value tests.
- Use coverage data to find under-tested user flows.
- Think from the customer POV to prioritize what real users actually touch.
With this information, testers can design a ranked list of tests: “These should be your P0s, these P1s.” You still review and adjust.
AI for Legacy Test Cleanup
TestWheel’s AI can help convert old test scripts (paragraph-style manual test cases) into useful, structured, automation-ready assets.
Simply download Excel sheets from TestWheel’s dashboard, populate them with requisite values, and reupload them. The platform will convert these values into pristine automation scripts that you can edit before execution.
The converted scripts carry clear preconditions, explicit steps, and verifiable expected results: the structure needed for future prioritization sequences.
AI for Automation Script Drafting
TestWheel’s AI engine converts manual test cases to automation scripts, but not the final version. Users can:
- Create UI test flows for web or mobile apps from natural language descriptions.
- Build API tests from endpoint definitions or existing manual cases.
- Generate data sets for load and performance scenarios.
- Generate data sets for load and performance scenarios.
Every test can be reviewed, and every assertion can be validated to match business expectations. The ability for human testers to refine and refactor tests over time is built into the pipeline by default.
This means that test case can be reworked according to changes in the product’s evolution, which will impact their spot in the prioritization hierarchy.
Test prioritization isn’t flashy, but ultimately controls if each release week feels calm and controlled or like a war zone.
Modern software shifts too fast for the “run everything and hope for the best” pipelines. Prioritization directs limited resources to the tests that matter. An AI-enabled tool like TestWheel furthers the process by picking up the grunt work: cleaning up old tests, surfacing risks, and suggesting which test should run first.
TestWheel will not replace testers, automate human instincts, or give you yet another fancy, no-meaning dashboard.
It will make testing feel lighter and cleaner.

